What Animals Does The Gaboon Viper Eat
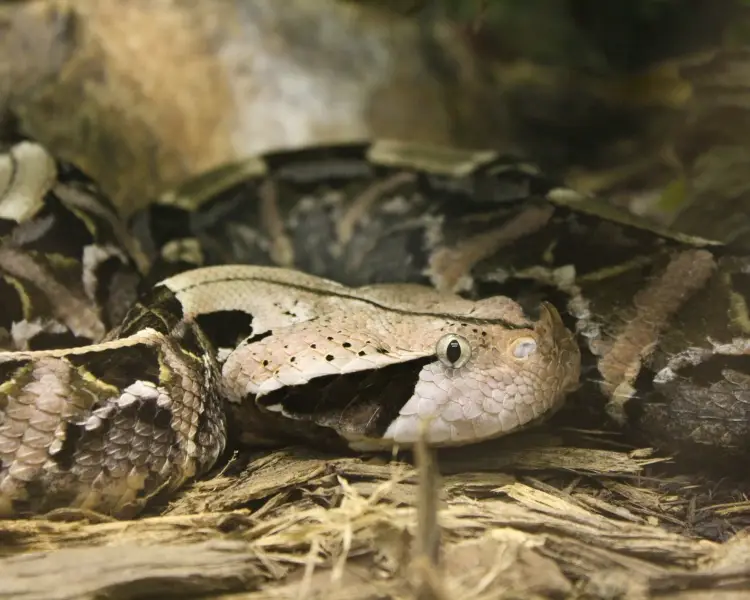



Gaboon Viper
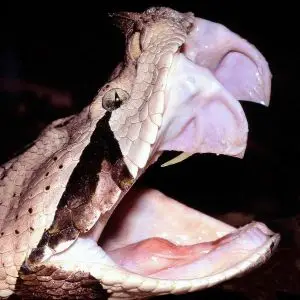
The Gaboon viper is a large venomous snake found in Sub-Saharan Africa. It has the longest fangs (upward to 5 cm) and the highest venom yield of any snake. The head is big and triangular, while the neck is greatly narrowed. A pair of "horns" is nowadays between the raised nostrils. The eyes are large and moveable. The color pattern consists of a series of pale, subrectangular blotches running down the center of the back, interspaced with dark, yellowish-edged, hourglass markings. The flanks have a series of fawn or brownish rhomboidal shapes, with light vertical central bars. The belly is pale with irregular brown or blackness blotches. The head is white or foam with a fine, dark central line, blackness spots on the rear corners, and a nighttime blueish-black triangle behind and below each centre. The iris colour is foam, yellow-white, orange, or silvery.
Photos with Gaboon Viper
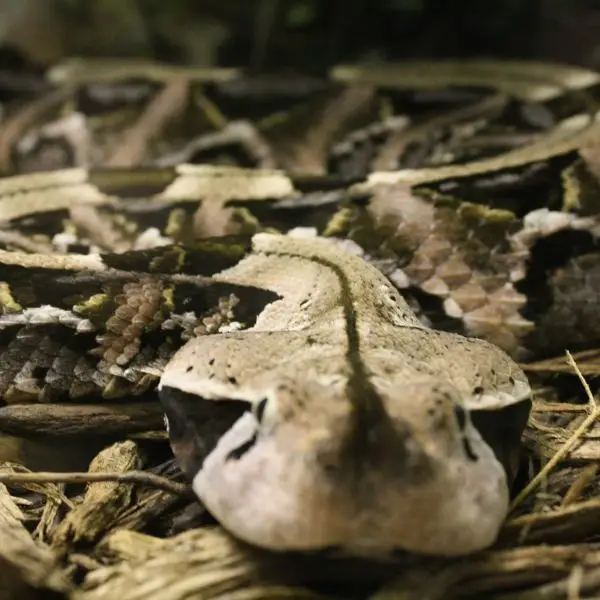




View 21 more photos of Gaboon Viper
Distribution
Geography
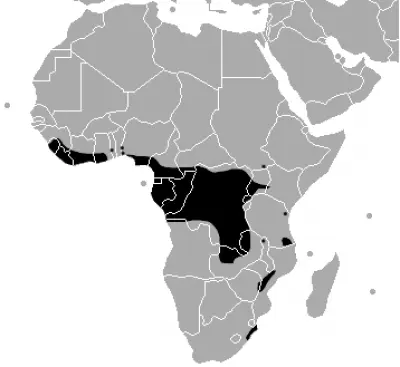
Republic of guinea, Ghana, Togo, Nigeria, Cameroon, Equatorial guinea, Gabon, DR Congo, Congo, Republic of angola, Testify More than Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania, Republic of zambia, Republic of malaŵi, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, South Africa, Sierra Leone, Republic of liberia Show Less
Gaboon vipers are found in Republic of guinea, Ghana, Togo, Nigeria, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabonese republic, Commonwealth of the Congo, DR Congo, northern Republic of angola, Central African Republic, Due south Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, eastern Tanzania, Zambia, Malawi, eastern Zimbabwe, Mozambique, northeast KwaZulu-Natal Province in South Africa and likewise in Sierra Leone and Republic of liberia in West Africa. Gaboon vipers are ordinarily plant in rainforests and nearby woodlands. In Tanzania, they are institute in secondary thickets, cashew plantations, and in agronomical state under bushes and in thickets. In Republic of uganda, they live in forests and nearby grasslands. They too exercise well in reclaimed woods areas: cacao plantations in West Africa and coffee plantations in Due east Africa. They have been found in evergreen forests in Zambia. In Zimbabwe, they only occur in areas of high rainfall along the forested escarpment in the eastward of the country. In general, they may also exist found in swamps, as well as in still and moving waters. They are commonly establish in agronomical areas near forests and on roads at nighttime.
Biome
Climate zones
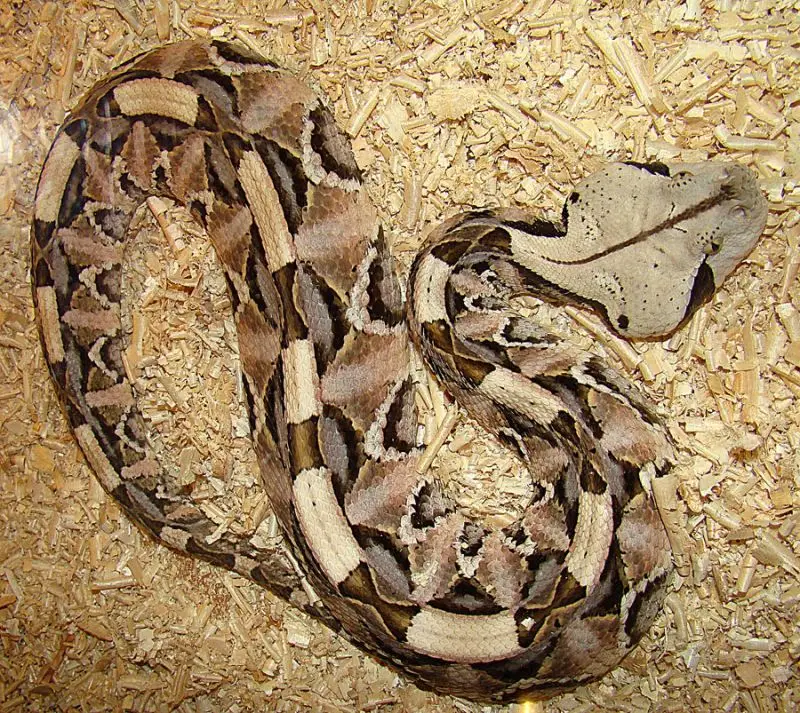

Habits and Lifestyle
Gaboon vipers are solitary and primarily nocturnal creatures. They take a reputation for being slow-moving and placid. They commonly hunt by ambush, often spending long periods motionless, waiting for suitable prey to pass by. Nevertheless, they may too hunt actively, mostly during the first six hours of the nighttime. They are unremarkably very tolerant snakes, even when handled and rarely seize with teeth or hiss, unlike most vipers. However, bites by bad-tempered individuals do occur. Locomotion is generally rectilinear, in a sluggish "walking" motion of the ventral scales. They may writhe from side to side when alarmed, merely only for short distances. If threatened, Gaboon vipers may hiss loudly equally a alarm, doing and then in a deep and steady rhythm, slightly flattening the caput at the expiration of each breath. Despite this, they are unlikely to strike unless severely provoked; however, they are one of the fastest hitting snakes in the earth.
Diet and Nutrition
Gaboon vipers are carnivores that feed on a diversity of birds and mammals, many different species of rodents, including field mice and rats, every bit well as hares and rabbits.
Mating Habits
Gaboon vipers brood between September and Dec. During this fourth dimension males engage in combat. This starts with one male person rubbing its chin along the back of the other. The 2d male will and so raise its head as high as possible. Equally they both do the same, the necks intertwine. When the heads are level, they plow towards each other and button. Their bodies intertwine equally they switch positions. They go oblivious to everything else, continuing even after they fall off a surface or into water. Sometimes they intertwine and squeeze then tightly that their scales stand up out from the pressure. They take also been observed to strike at each other with mouths closed. Occasionally, the combatants will tire and break off the fight by "mutual consent", resting for a while earlier resuming again. The event is settled when one of the two succeeds in pushing the other's caput to the ground and raising its own by xx-thirty cm. Females usually give birth to viii-43 alive young in late summer. Gestation takes near seven months. Snakelets are 30 cm long at nascence and don't need parental care.
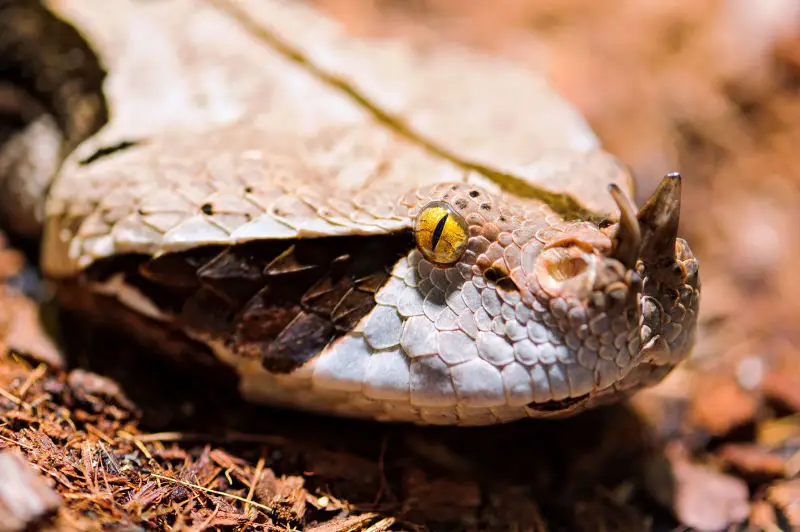

Population
Population threats
There are no major threats to Gaboon vipers at present.
Population number
Soon, the Gaboon viper is non included in the IUCN Red Listing and its conservation condition has non been evaluated.
Ecological niche
Due to their diet habits, Gaboon vipers play an important role in their ecosystem; they assistance to command populations of rodents.
References
More than Fascinating Animals to Learn About
Source: https://animalia.bio/gaboon-viper
Posted by: perryhounts.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Animals Does The Gaboon Viper Eat"
Post a Comment